Ask any online seller in India, and you’ll hear the same thing: making a sale isn’t the toughest part, but delivering is. The real struggle begins right after the customer taps “Order Confirmed.”
Logistics challenges are late deliveries, wrong courier assignments, damaged parcels, inaccurate addresses, and COD refusals erode margins, hinder growth, discourage repeat purchases, and make scaling costly.
We’ve watched this play out across India’s fast-growing e-commerce brands. Some businesses doubled their revenue without new campaigns, heavy discounts, or even expanding their product range. All they did was strengthen their logistics, fixing warehouse placement, courier selection, packaging quality, and RTO prevention.
And once they stopped treating logistics as a cost center and started treating it as a growth strategy, two things changed instantly:
- Their delivery costs decreased while their order volume increased.
- Their customer loyalty increased without running discounts or offers.
In a market where countless sellers offer similar products, your real differentiator isn’t what you sell, it’s how you deliver.
This guide breaks down logistics management as a strategic lever for Indian e-commerce and D2C businesses, grounded in reality rather than textbook theory.
What Is Logistics Management? (And Why It Matters for Sellers)
Logistics management involves planning, executing, and controlling the movement of goods from your warehouse to the customer’s location, ensuring they remain safe throughout the journey and that the right item reaches the right buyer, without damage, at the right time, for the lowest possible cost.
It matters for e-commerce products not to produce or source, but to get the product delivered safely, on time, and at a lower cost, as even the best products can get stuck in transit, return pipelines, or poor warehouse management, costing you money and reputation.
In other words, logistics management in e-commerce is the end-to-end handling of storage, shipping, and returns at the lowest possible cost.
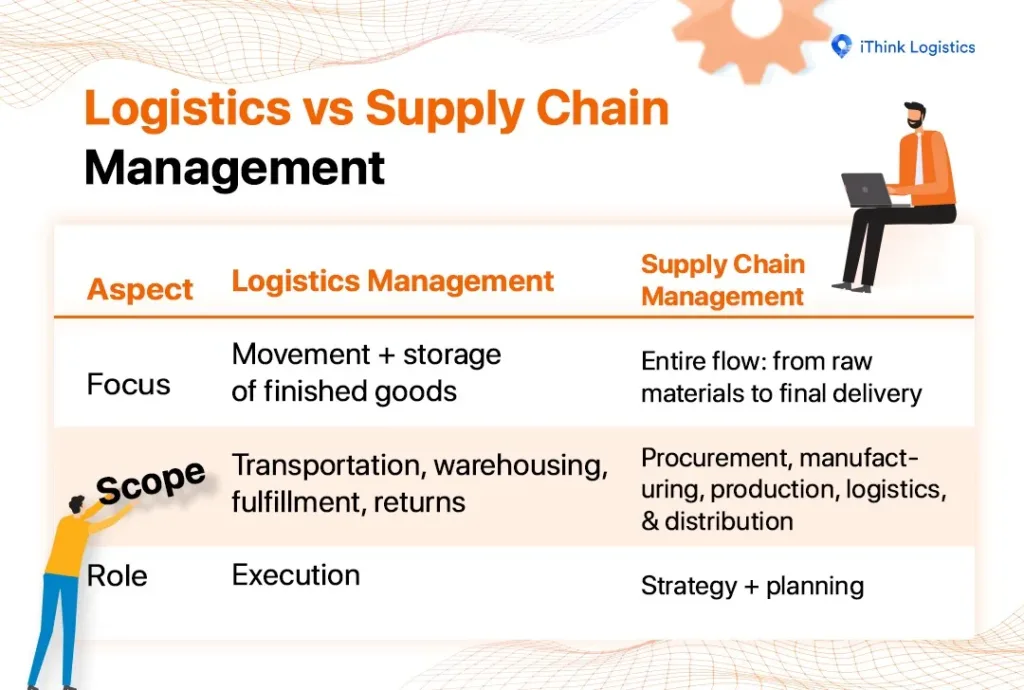
Logistics vs Supply Chain Management
So, what is logistics and supply chain management for e-commerce sellers? Many sellers use “logistics” and “supply chain” as if they were interchangeable. In practical business terms, however, they are different:
In simple terms, logistics and supply chain management work together. Supply chain management sets the strategy, while logistics executes it.
Put simply, the supply chain provides the strategy (‘the brain’), while logistics provides the action (‘the muscle’). Even the smartest strategy fails without strong action.
Why Logistics Management Is Crucial for Indian E-Commerce Sellers
The importance of logistics management goes far beyond delivery; it directly affects profitability, brand trust, and repeat orders. In India, online buyers don’t return because the product was bad; they return because it arrived late, arrived damaged, or didn’t arrive at all.
For this reason, logistics now drive revenue—not just delivery expenses.
Industry studies show:
- More than 55% of online shoppers leave their carts if delivery timelines are slow or uncertain.
- A study referenced by Peasy (e-commerce insight blog) shows that customers who rate their delivery experience “excellent” are 2.4× more likely to make repeat purchases.
- According to Eshopbox, one key strategy to reduce RTO is to expedite shipping and improve logistics.
This means warehouse location, courier selection, address verification, and tracking transparency directly impact:
- Profitability
- Repeat purchases
- Customer satisfaction
- Return rates (RTO)
- Brand perception
Your product delivery experience matters more to your customers than your product quality does. Even if a competitor has a better product, you will still win the market if the competitor’s delivery experience is very bad.
The Core Objectives of Logistics Management for E-Commerce
Focus on these key objectives: deliver products quickly and reliably.
- Minimize delivery and storage costs.
- Avoid stockouts or overstocking.
- Reduce damage and returns.
- Enhance transparency and tracking for customers.
- Build a scalable return & reverse logistics mechanism.
- Use real-time data to drive decisions.
Aligning logistics with these goals transforms the supply chain into a lean, efficient, and profitable growth engine.
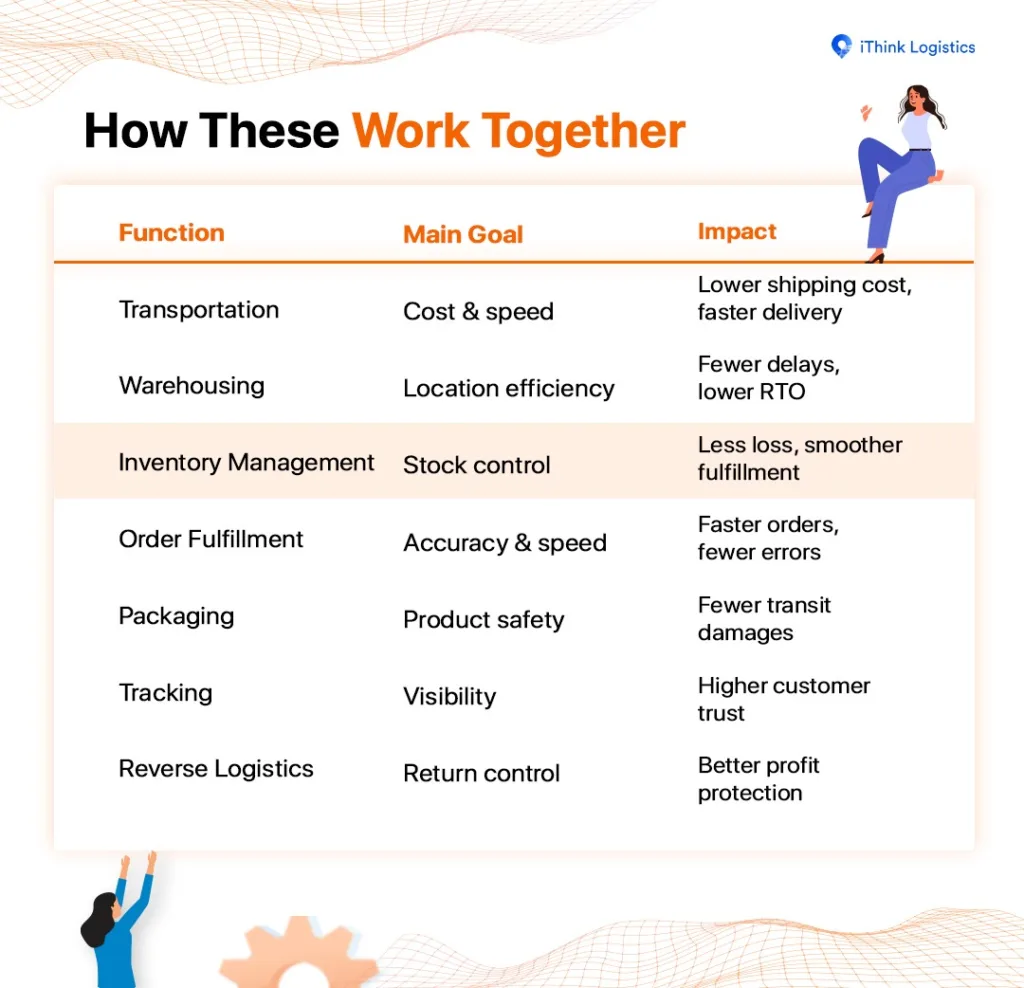
Key Functions & Components of Logistics Management
Below are the essential functions and their components:
1. Transportation Management
Function: Moves goods between suppliers, warehouses, and customers
Core Components:
- Route planning
- Courier partner allocation
- Freight cost optimization
- Mode choice (air, road, rail, ocean)
Transportation accounts for nearly 50–60% of total logistics costs in India, while for Sweden it’s 30% around and for South Korea it’s 70% of total cost.
2. Warehousing & Storage
Function: Safe storage and efficient movement of goods
Core Components:
- Warehouse location planning (near demand clusters)
- Inventory zoning & picking flow design
- Safety stock & climate control for sensitive products
Strategically placing warehouses shortens delivery distances and speeds up shipping. This helps reduce RTOs and improve customer satisfaction.
3. Inventory Management
Function: Ensures the right stock quantity at the right time
Core Components:
- Demand forecasting
- Reorder planning
- Buffer stock management
- SKU-level inventory tracking across warehouses
This is important: overstocking raises holding costs, while understocking results in lost sales and delivery delays due to back-ordering.
4. Order Fulfillment
Function: Manages the journey from order placement to customer delivery
Core Components:
- Order receiving and prioritization.
- Picking, packing & dispatch
- Allocation to the best courier partner
A streamlined fulfillment process leads to fewer errors, faster deliveries, and better customer experiences.
5. Packaging & Handling
Function: Safeguards product integrity and enhances brand value
Core Components:
- Material selection (corrugated, bubble wraps, tamper-proof bags)
- Right-size packaging to reduce volumetric weight
- Fragile handling, cushioning & labeling
Evidence shows that poor packaging often causes transit damage and product returns. This is why packaging should be considered a key logistics investment rather than just an expense.
6. Information Flow & Tracking
Function: Enables visibility and decision-making across the supply chain.
Core Components:
- Real-time tracking
- Proof-of-delivery (POD) systems
- Automated customer notifications
- Order, return & shipment analytics
Transparent tracking reduces customer inquiries like ‘Where is my order?’ It builds customer trust and reduces operational friction.
7. Reverse Logistics
Function: Handles returns, exchanges, recycling & resale.
Core Components:
- Pickup scheduling & return shipping
- Inspection & re-packaging
- Refund or exchange management
- Non-delivery resolution (NDR) system
India has one of the highest RTO & return rates globally, especially for COD orders. A strong reverse logistics process protects profits and enhances customer lifetime value.
How These Work Together
Types of Logistics Models That Work for Indian E-Commerce
Depending on your business stage and product mix, you can use or combine:
1. Inbound Logistics
Inbound logistics focuses on moving goods from suppliers to your warehouse or fulfillment center.
It includes activities such as:
- Raw material procurement (for manufacturers)
- Finished goods supply from brands/distributors (for sellers)
- Freight coordination and storage planning
Why it matters for e-commerce sellers: Strong inbound logistics keep your shelves stocked, stop backorders before they happen, and help you list your fast-moving products confidently without worrying about stockouts.
Example: Brands using regional procurement hubs shorten replenishment time, helping them maintain stock during sale seasons like Big Billion Days or Amazon Great Indian Festival.
2. Outbound Logistics
Outbound logistics is about delivering the final product from your warehouse to the customer.
It involves:
- Order processing
- Picking and packing
- Courier selection
- Shipment tracking & final delivery
Why it matters: Fast and accurate outbound logistics directly influence:
- Customer reviews
- Repeat purchases
- RTO rates (especially in COD)
In India, the winner is rarely the brand with the best product… It’s the one that delivers faster, safer, and more transparently.
3. Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics deals with products moving from the customer back to the seller.
It includes:
- Returns (refunds/exchange)
- Repair or refurbishing
- Repackaging and resale
- Disposal/recycling of unsellable units
Why it matters: India records some of the highest return rates in the world, especially in categories such as apparel, footwear, and accessories, as well as COD orders.
- Reduce loss from damaged returns.
- Recover value through refurbishing or resale.
- Improve customer retention with hassle-free returns.
For an online customer, an “easy return experience” is as crucial as delivery speed.
4. Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
3PL refers to outsourcing logistics operations to expert companies that handle fulfillment, warehousing, shipping, and returns.
What 3PLs usually offer:
- Multi-location warehouses
- Courier allocation engine
- Automated tracking and NDR/return systems
- Packing, labeling & order processing
Why e-commerce brands choose 3PL: Brand outsourcing logistics to free up time to focus on product, marketing, and growth while experts handle storage, fulfillment, and delivery.
Example: Many D2C brands moving from 50 to 5,000 orders a day shift to a 3PL because it lowers their delivery costs and helps them manage order spikes during sale seasons without problems.
5. Fourth-Party Logistics (4PL)
4PLs take logistics outsourcing one step further. They don’t just execute logistics; they strategize, manage partners, optimize the supply chain, and make data-driven decisions on your behalf.
They handle:
- Complete supply chain design
- Vendor coordination (warehouses + couriers + tech)
- Logistics analytics and cost restructuring
Who needs 4PL? Brands scaling nationwide or internationally, where logistics becomes a strategic function, not just operational.
6. Ecological (Green) Logistics
Green logistics focuses on reducing the environmental impact of logistics activities.
It includes:
- Reusable / recyclable packaging
- Consolidated shipments to reduce carbon footprint
- Smart routing to reduce fuel use
- Recycling returned items
Why it matters today: Consumers are choosing brands that operate responsibly and sustainably, so investing in eco-friendly logistics not only reduces your environmental impact but also strengthens long-term customer trust and reduces waste-related costs.
Step-by-Step Logistics Process: From Order to Delivery (and Back)
Below is the step-by-step logistics journey described from order to delivery in details:
1) Procurement: Sourcing Products
Before anything can be sold, products must be sourced from wholesalers, manufacturers, or raw material suppliers.
Key activities:
- Negotiating prices and lead times
- Checking product quality
- Planning seasonal and bulk purchases
- Aligning supplier capacity with forecasted demand
Why it matters: Strong procurement avoids stock delays, improves product quality, and reduces manufacturing or buying costs.
2) Warehousing: Storing Goods Smartly
Once products arrive in the warehouse, they get organized for fast picking and dispatching.
- Receiving and verifying stock
- Organizing items by SKU, size, or demand
- Segregating fast-moving products into pick zones
- Maintaining safety stock
Smart warehousing equals fewer errors, faster shipping, and better order accuracy.
3) Inventory Management: Maintain Stock Levels
Too much inventory drains cash. Too little inventory kills sales. Inventory management requires a balanced approach in:
- Tracking stock in real time
- Forecasting demand for the upcoming months
- Setting reorder alerts when stock dips
- Avoiding dead stock (slow-moving units)
4) Order Fulfillment: Turning an Order into a Shipment
When a customer clicks “Buy Now,” a structured backend process begins.
Order fulfillment includes:
- Order Processing: The system verifies payment, SKU availability, and address.
- Picking: Warehouse staff locates the product (often using barcodes or mobile scanners).
- Packing: Items are packaged safely in size-appropriate boxes, with cushioning and branding elements.
Strong fulfillment reduces damage returns, customer complaints, and negative reviews.
5) Transportation & Delivery: Reaching the Customer
Once packed, the order moves from the warehouse into the delivery network. This phase is the customer’s first physical interaction with your brand.
It includes:
- Selecting the best courier based on location, cost, serviceability, and speed
- Dispatching shipments for first-mile pickup
- Managing tracking updates and delivery attempts
- Completing last-mile delivery to the doorstep
Delivery speed and reliability directly influence repeat orders and brand loyalty.
6) Reverse Logistics: Handling Returns Efficiently
Not every product delivered stays with the customer. Managing returns responsibly protects revenue and customer trust.
Reverse logistics activities:
- Return pickup and tracking
- Inspection for damage or resale potential
- Repackaging or refurbishing, if possible
- Issuing refunds or replacements
Smooth returns build customer confidence and increase conversions on COD and high-value orders.
7) Analysis & Optimization: Continuous Improvement
The best logistics strategies evolve with data, not assumptions.
Brands should continually track:
- Delivery time vs. promised time
- RTO (Return-to-Origin) percentage and reasons
- Courier performance by pin-code
- Customer feedback on delivery & packaging
- Warehouse picking accuracy
Continuous optimization reduces hidden costs and transforms logistics into a profit driver.
How a Logistics Management System Helps You Scale
To manage this complexity, you need a Logistics Management System (LMS), the digital brain behind your operations.
Key features:
- Dashboard & Analytics: Track delivery SLA, courier performance, return rates
- Automated Courier Allocation: Based on performance, pin codes, and cost
- Warehouse Management (WMS): Real-time stock location, picking logic
- Order Management: From your store or marketplace → fulfillment
- Return Management: Capturing reason codes, automating RTO pickup or inspections
- Notification Engine: For customers (tracking updates) + operations team
Sellers who adopted a robust LMS (Logistics Management System) saw reductions in logistics costs and improvements in first-attempt delivery success, per our internal analysis.
Common Logistics Challenges in Indian E-Commerce & How to Overcome Them

Why Logistics Management Is Your Competitive Advantage
For e-commerce sellers in India, logistics isn’t just about moving parcels, it’s about building:
- Trust: Prompt, reliable delivery makes customers come back.
- Efficiency: Smarter logistics = lower costs without compromising service.
- Scalability: With a strong logistics system, you can expand across geographies and SKUs.
- Resilience: You can handle returns, pin-code failures, and courier issues proactively.
While many sellers try to win only on pricing or marketing, the real winners are those who master logistics.
Final Thoughts
- Audit your current logistics: Look at delivery costs, returns, courier mix, and warehouse locations.
- Adopt a Logistics Management System (LMS): Start small, scale gradually.
- Use data to decide everything: Choose couriers, set up warehouses, and manage inventory, all based on real metrics.
- Plan for returns and reversals: Don’t ignore returns, build processes, and don’t panic.
- Continually optimize: Review performance monthly; tweak courier mix, routing, inventory, and packaging.
When logistics becomes your growth engine, not just a cost center, your business gains. You spend less, deliver faster, keep customers happier, and scale smarter.
FAQs
Q.1: What is logistics management?
A: Logistics management is planning and controlling how products move from your warehouse to customers, including storage, shipping, and returns, in the most efficient and cost-effective way.
Q.2: What are the functions of logistics management?
A: The main functions are transportation, warehousing, inventory management, order fulfillment, packaging, information flow, and reverse logistics.
Q.3: What are the objectives of logistics management?
A: They include delivering on time, reducing cost, optimizing inventory, minimizing damage, improving satisfaction, and creating a scalable return system.
Q.4: What does a logistics management system do?
A: An LMS evaluates and allocates couriers, tracks delivery performance, manages warehouse inventory, processes returns, and provides real-time analytics so you can make data-driven logistics decisions.
Q.5: Why is logistics management so important for e-commerce?
A: Because in e-commerce, delivery experience is customer experience. Great logistics means fewer failed orders, lower returns, better reviews, and more repeat buyers.











Leave a Reply